While men once searched for the fountain of youth in foreign jungles and far-off lands, these days we expect it to come in pill-form. One of the more promising candidates is called nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide or NAD.
It’s a crucial compound for powering cells, but we’re starting to realize it may have all sorts of benefits, even reducing the effects of aging. There is some evidence for those claims, but we’re not yet sure if it works as advertised or is just another myth.
Key Takeaways
- NAD supplements are generally safe
- Research shows NAD supplementation is effective for some health problems
- Helps older folks stay active and healthy
- NAD plays an important role in the body
- May help with mental health issues like addiction or depression
NAD+ Overview: Coenzyme or Cofactor?
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is almost an enzyme, but not quite. In this case, some enzymes also have compounds that make them more efficient, sort of like another catalyst. These extra-catalyzing compounds are called coenzymes.
Coenzymes are one type of cofactor, which is a general term for a helper molecule. NAD+ Is therefore both a coenzyme and a cofactor. It is required for some of the most important biological processes in the body, such as cellular metabolism. Recent scientific research has also shown it has a role to play in aging and general health.
Our bodies make all the NAD+ cells require to function properly. It does this through one of three metabolic ‘pathways,’ chains of chemical reactions that turn simple compounds into more complex ones, or vice versa [1]. The three pathways are:
- De novo or kynurenine pathway: NAD+ is synthesized by combining simpler compounds from outside the human body, specifically the amino acid l-tryptophan.
- The Preiss-Handler pathway: Similar to the de novo pathway, but starting with a different compound, nicotinamide acid.
- The salvage pathway: NAD+ is formed by putting back together byproducts from previous reactions including nicotinamide (NAM), nicotinamide riboside (NR), and Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN).
How Does It Work
NAD is primarily used in the human body for providing cellular energy in metabolic processes called redox reactions. The first part of redox comes from reduction, which is the process of donating electrons to other cells. The second part comes from the term oxidation, in which electrons are taken from elsewhere.
There are two different forms of NAD, one that is neutrally charged with an electron to spare, called NADH. The other version is NAD+, with the plus indicating it’s lacking an electron. The back and forth of the two help maintain cellular homeostasis, a sort of constantly shifting stability.
These electron trades are part of the cell’s energy metabolism, with NAD playing the part of middleman and carrying electrons back and forth. While important, the process takes a toll on the cell, a trade-off that is called oxidative stress (OS). This is the oxidative stress all those antioxidant advertisements are talking about.
Its use in metabolic reactions is important. However, NAD+ has uses elsewhere in the body and it’s these functions that generally get people excited. In particular, NAD plays a role as a substrate, a base upon which to build other enzymes.
What It Does
Science is only starting to guess at the effects of NAD+ on human biology. However, it’s hypothesized that most of those effects are the result of NAD+ being used to build other enzymes. These new enzymes have uses everywhere in the body, helping along reactions that govern things like:

- Stress response
- Insulin sensitivity
- Circadian rhythm
- Immune activity
- Inflammation
The supply of NAD+ can also affect DNA repair, gene expression, and healthy cell growth, all of which are relevant to aging. Additionally, the ratio between NAD+ and NADH can be used as a measure of OS in the cell.
NAD+ and Mental Health
The last century or so has seen tremendous progress in the diagnosis and treatment of mental health issues. However, the physiological causes of mental illness have largely remained a mystery.
That may be beginning to change, as schizophrenia, depression, anxiety, and addiction have all been linked to factors that disrupt brain function, including:
- Oxidative stress
- Impaired cellular metabolism
- Inflammation in the brain
- Cellular health through immune response
We mentioned that the ratio of the two forms of NAD, NAD+ to NADH, is used as a rough measure of OS. Interestingly, it may also be a physiological indicator of mental health issues. You have to measure the ratio in the brain of a living patient, which is tough.
It’s been done, however, using a new method called in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). Using the magic of magnetic fields, this technique allows scientists to get an idea of the chemical reactions going on in your brain without having to crack it open [2].
The results seem to bear out the hypothesis, with one example showing that sufferers of schizophrenia had a higher degree of OS in their frontal lobes.
That’s just one way NAD might be able to impact brain function and mental health.
Sobriety and Satiety
While it may seem like COVID-19 has held the world hostage for an eternity, we’ve actually been struggling with two other epidemics for much longer: opioids and obesity.
In different ways, both are a form of addiction, though they seem quite different from each other. It’s becoming clear that the physiology behind addiction may be largely the same, whether you’re struggling with substance abuse or constant food cravings.
There are several ways in which NAD+ is wrapped up in the biology of addiction. It helps produce ATP, for example, which is turned into happy chemicals by opiate receptors when heroin users shoot up [3]. As a result, it has been investigated for use in helping people kick their addictions [4].
In particular, using NAD+ has helped people control cravings for their addiction, whatever it is. One of the most difficult aspects of addressing addiction is managing cravings. Depending on the severity of the addiction, cravings can be stronger than addicts can control. NAD+ can blunt the strong cravings, making them easier to resist.
Furthermore, it can be useful in controlling other aspects of withdrawal, such as tremors and pain. It can also help manage some of the emotional distress. While it’s not an official treatment, IV NAD+ treatments have been used for years to help addicts in withdrawal.
Depression and Anxiety
Depression and anxiety have both been strongly associated with OS, and therefore with levels of NAD+ and NADH. The redox reactions that require NAD are necessary for life. However, the byproducts of oxidation, called free radicals, are toxic. OS is actually the damage that is caused by those free radicals, the same ones from antioxidant ads [5].
The idea that at least some mental illnesses are caused by OS is a new one. There’s a lot of work that still has to be done to understand the link. At the moment, much of the evidence is based on animal studies, which are obviously only approximations of human patients.
However, some human clinical trials have shown that the connection isn’t completely out of the question. Some natural antioxidants, for example, the compound albumin, are found to be lower in people diagnosed with depression. Other markers for OS have also been found in people who suffer from anxiety and depression.
Some medications for depression and anxiety have been tested for antioxidant properties. However, there hasn’t been any clear evidence that they do affect levels of free radicals or repair OS damage.
As a result, more investigation needs to be done before we can make a clear link between OS, NAD, and mental health concerns.
NAD+ and Aging
If there is a connection between mental illness and OS, then it’s possible OS also plays a role in cognitive decline due to aging. Failing mental clarity may not be the only age-related damage we can blame on OS.
In fact, OS is one of the top candidates for the physiological cause of aging and age related diseases. It may sound strange, but we’re not entirely sure how aging happens, other than that it appears to be a gradual accumulation of damage.
In particular, damage to the structures that build new cells and repair old ones, so mistakes are introduced that don’t get fixed. This can cause several problems, such as reducing the efficiency of the body’s functions down to the molecular level. All of that damage is the sort that OS can cause.
Additionally, NAD+ other functions, as a substrate for enzymes and as a signaling molecule, may play an even greater role in aging.
That doesn’t necessarily mean changing NAD+ levels can impact the aging process. However, there’s other evidence that the level of NAD+ in your body is related to the aging process.
NAD+ Levels Reduce With Aging
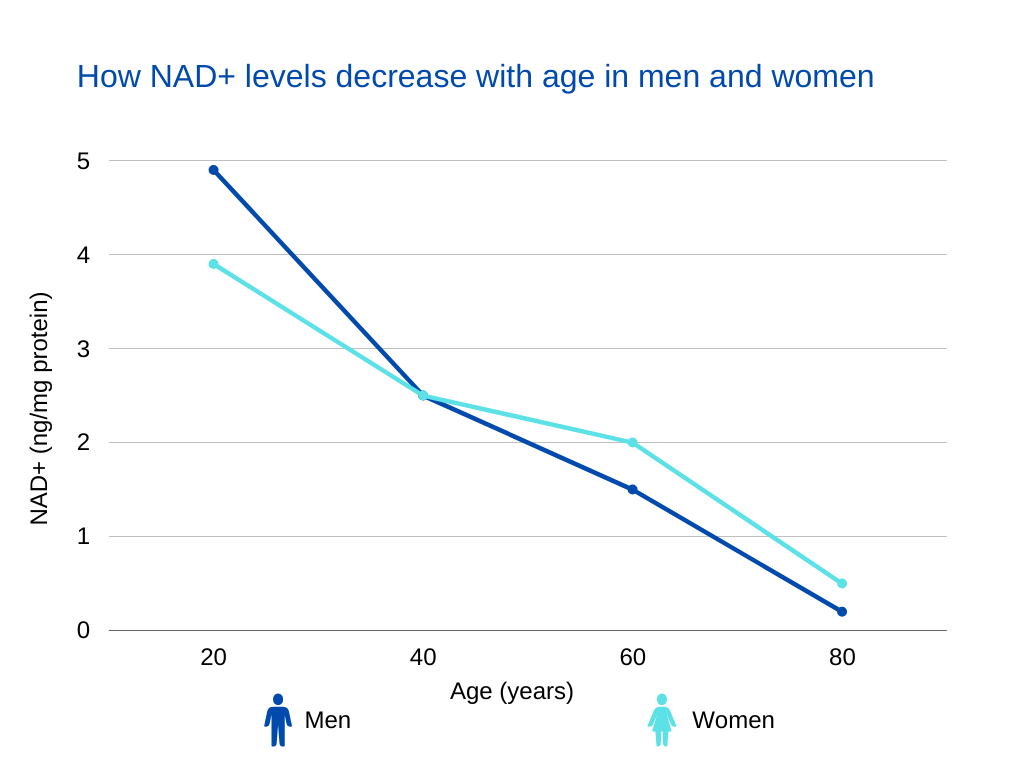
There’s no question that NAD+ levels drop as we age. By the time we reach middle age, NAD+ levels could be half what they were during our younger years. This decrease can increase OS, as we’ve discussed, as well as cause a few other problems.
It’s not entirely clear why NAD+ levels drop. One hypothesis is that our bodies simply stop making as much, for one reason or another. Other research shows that some NAD+ may be turned into compounds that disrupt the cell’s function [6].
Does NAD+ decrease faster in men or women or is there no difference between genders?

What Happens When NAD+ Levels Are Reduced?
Lower NAD+ means more oxidative stress. NAD+ has other roles to play also, helping to protect DNA, repair mistakes, and prevent the formation of tumors. Together, the effects are not only noticeable on the level of day-to-day living, they can be debilitating.
Lowered NAD+ levels are associated with neurodegenerative and age-related diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease [7]. The risk of diabetes is also increased, as is the risk of cancer. Your overall metabolism may also be affected, making it more difficult to manage or lose weight.
NAD+ Supplements and Its Anti-Aging Effects
When talking about aging, health professionals and researchers sometimes distinguish between your lifespan, the length of your life, and healthspan. Healthspan is a bit more complicated to define, but it refers to good health. Your healthspan is the part of your life you’re able to be both physically active and mentally clear.
Interestingly, using a NAD supplement seems to improve healthspan, without necessarily impacting lifespan. In other words, NAD supplementation may slow the aging process without extending your life [8].
The risk of age-related disease was generally lowered, but it specifically impacted neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Risk factors for heart disease and cancer were lowered. Additionally, older individuals found it easier to maintain muscle tone, keep off weight, and stay active.
Oral supplements are one option, though in most cases it’s not going to be oral nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Instead, oral and parenteral applications are more likely to be the ingredients for making NAD, like nicotinic acid, NR, NMN, and NAM.
Metabolism and Energy
It’s clear that NAD plays a crucial role in metabolism, redox reactions, and the Krebs cycle. As NAD+ levels drop due to aging, however, all of those processes begin to slow and become less efficient. Since NAD+ is so crucial, not having enough is a problem.
While all of those processes happen on the molecular level, the cumulative effect is noticeable in daily life. The reverse is also true, as preliminary evidence shows that supplementing NAD can improve metabolism and energy levels among older individuals.
Side Effects
Scientific research hasn’t revealed any serious side effects, though there is still plenty of studies to be done. A high dose of NAM in one study resulted in headaches and dizziness, but no serious or long-term side effects have been revealed [9]. Supplementing NAD seems to be fairly safe.
NAD Therapy
Unlike supplements, NAD therapy is delivered by intravenous (IV) drip. For decades, NAD IV therapy was used as an unofficial treatment for addiction. However, due to research connecting NAD to all the other factors we’ve discussed, it’s now being offered in other contexts as well.
It’s important to remember, though, that those other connections have only been understood in the last couple of years. While NAD IV therapy has been used for addiction therapy for years, it’s never been properly assessed or approved by the FDA.
Despite that, businesses around the country have begun offering NAD IV therapy as a treatment for a variety of issues. Not all the outcomes have been positive, suggesting we don’t fully understand the effects [10].
What Is NAD+ Therapy?
Oral nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide isn’t usually as effective as supplementing the ingredients of NAD. When you ‘eat’ NAD, it is broken down into parts and reassembled later for use. Taking precursors like nicotinamide acid skips a step, so it’s more efficient.
When the drug administration is done through IV therapy, however, NAD+ can be put directly into the bloodstream for use by the body. In theory, that should be easier to use and be more effective [11].
IV Therapy is usually a course of treatment, with two treatments a week for four weeks. That’s followed by maintenance treatments less frequently.
One of the more popular uses for NAD IV therapy is as part of a substance abuse therapy program. IV treatment has also been offered as a treatment for chronic fatigue syndrome and other medical conditions. Unfortunately, solid evidence supporting those uses remains lacking.
Benefits of NAD+ Therapy
As you may have gathered, it’s tough to give a definitive list of potential benefits. The use with the most evidence backing IV therapy up is in addiction recovery. Those who recommend the treatment say that IV therapy can:

- Reduce or eliminate cravings
- Reduce symptoms of withdrawal
However, IV therapy isn’t universally effective. Additionally, the effects of withdrawal can be dangerous and it’s not clear that NAD therapy reduces that risk.
Other uses are based on the other connections we’ve already discussed, such as benefiting mental health, reducing the signs of aging, and improving energy levels. NAD supplementation has been shown to have some of these effects. However, at the moment it’s tough to know whether any particular person may experience these benefits, or to what extent.
What To Expect During NAD+ Infusion
In broad strokes, NAD IV therapy is similar to other IV treatments. A line is inserted into a vein and then a solution of NAD and saline is administered. The therapy may take several hours, depending on the treatment plan.
You may feel cold while the IV therapy is being administered and an urge to use the restroom is common. An infusion is a slow method of drug administration. However, if the NAD is pushed too quickly, you may end up with some discomfort in your chest, stomach, or head [12].
Danger signs to look out for include:
- Swelling of the vein
- Breathing problems
- Redness or bruising where you were poked
- Dizziness
- Chest pains
The chances of serious side effects from NAD IV therapy seem to be quite low.
NAD+ Therapy vs Supplements
NAD IV therapy is billed as a more efficient or effective way to supplement NAD+. Evidence does seem to point that way, with studies showing that there is a higher level of NAD+ across the body after IV treatment.
The full effects aren’t understood, however. Doses delivered through IV tend to be higher and therefore have a higher chance of side effects. Liver function may have been impaired by IV therapy, for example.
NAD supplementation, either orally or by IV, and its effects on biological processes is not fully understood. Comparing the two, or assessing the safety of NAD+ treatment generally, is therefore difficult.
FAQ
The effect of NAD is a complex subject, but it does have the potential to be genuinely effective. To help clear up some confusion, we’ve answered some common questions.
Does NAD+ Really Work?
Unfortunately, it’s impossible to give a straight ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ at this point. There is a lot of promising evidence that says it can be effective for a range of different uses. In particular, it has been shown to increase energy and mental clarity in older folks in only a few minutes. Its success in treating other conditions is unclear.
It’s also probably not useful as an exercise supplement, particularly for younger people.
How Long Does NAD Therapy Last?
A single session of therapy can last several hours as the NAD is administered slowly.
It’s difficult to say how long the treatment will remain effective, as treatments vary. Also, we simply don’t understand all the factors that come into play.
How Can I Increase My NAD+ Naturally?
You can definitely increase your NAD+ naturally. There are a few ways to go about it:
- Calorie restriction: One of the best ways to up NAD+, and to stave off the effects of aging in general, is restricting calorie intake. Try to eat enough to stay healthy while not overdoing it.
- Exercise: Increasing activity will also up the amount of NAD+ in your body.
- Healthy sleep routine: It’s not just the amount of sleep you get, but also establishing a regular pattern of sleep and wakefulness [13].
Can NAD Reverse Aging?
Supplementing NAD has been shown to have some positive effects for older people, such as improving mental clarity, metabolism, and other factors. That’s not quite the same thing as reversing the aging process, though it can help you stay healthy and active longer.
How Much Does NAD Therapy Cost?
NAD IV therapy can be very expensive, costing as much as $15,000. It’s a lot of money and there’s no guarantee it will work.
Conclusion
A lot of supplements get hyped way beyond what the evidence shows. This is true of NAD+, but unlike a lot of snake oil supplements, there may be some truth to its benefits as well. It’s a promising area of research, though it’s never a bad idea to be cautious when it comes to the hot new health trend.
References:
- Lin, Huawen, et al. “Synthesizing and Salvaging NAD+: Lessons Learned From Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii.” PLOS Genetics, Public Library of Science, 9 Sept. 2010, journals.plos.org/plosgenetics/article?id=10.1371%2Fjournal.pgen.1001105.
- Kim, Sang-Young, et al. “Redox Dysregulation in Schizophrenia Revealed by in VIVO Nad+/Nadh Measurement.” OUP Academic, Oxford University Press, 24 Sept. 2016, academic.oup.com/schizophreniabulletin/article/43/1/197/2503778?login=true.
- Kosten, Thomas R, and Tony P George. “The Neurobiology of Opioid Dependence: Implications for Treatment.” Science & Practice Perspectives, National Institute on Drug Abuse, July 2002, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2851054/.
- Braidy, Nady, et al. “Sobriety and SATIETY: Is NAD+ the Answer?” Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland), MDPI, 14 May 2020, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7278809/.
- Ng, Felicity, et al. “Oxidative Stress in Psychiatric Disorders: Evidence Base and Therapeutic Implications.” OUP Academic, Oxford University Press, 1 Sept. 2008, academic.oup.com/ijnp/article/11/6/851/671366.
- Schultz, Michael B, and David A Sinclair. “Why Nad(+) Declines during Aging: It’s Destroyed.” Cell Metabolism, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 14 June 2016, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5088772/.
- Hikosaka, Keisuke, et al. “Implications of NAD Metabolism in Pathophysiology and Therapeutics for Neurodegenerative Diseases.” Taylor & Francis, 7 July 2019, www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/1028415X.2019.1637504.
- Mehmel, Mario, et al. “Nicotinamide Riboside-The Current State of Research and Therapeutic Uses.” Nutrients, MDPI, 31 May 2020, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7352172/#B149-nutrients-12-01616.
- Radenkovic, Dina, et al. “Clinical Evidence for Targeting Nad Therapeutically.” MDPI, Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute, 15 Sept. 2020, www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/13/9/247/htm.
- Harper, Jake. “Addiction Clinics Market Unproven Infusion Treatments to Desperate Patients.” NPR, NPR, 22 Aug. 2019, www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2019/08/22/741115178/addiction-clinics-market-unproven-infusion-treatments-to-desperate-patients.
- Grant, Ross, et al. “A Pilot Study Investigating Changes in the Human Plasma and Urine NAD+ Metabolome during a 6 Hour Intravenous Infusion of NAD.” Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, Frontiers Media S.A., 12 Sept. 2019, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6751327/.
- “IV Treatment at Home: Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia.” MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000496.htm.
- Poljsak, Borut, et al. “Healthy Lifestyle Recommendations: Do the Beneficial Effects Originate from Nad+ Amount at the Cellular Level?” Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, Hindawi, 12 Dec. 2020, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7752291/.

Leave a Reply